SaaS software as a service is reshaping the landscape of how businesses access and utilize technology. Unlike traditional software, which often requires hefty one-time purchases and installation on local devices, SaaS operates on a subscription model that emphasizes cost-effectiveness, scalability, and ease of access. This guide delves into the SaaS model, exploring its myriad advantages and potential limitations, enabling business owners to make informed decisions about their software needs.
Toc
- 1. Understanding the SaaS Business Model
- 2. Key Characteristics and Benefits of SaaS
- 3. Popular SaaS Applications and Examples
- 4. Related articles 01:
- 5. Choosing and Implementing the Right SaaS Solution
- 6. Related articles 02:
- 7. SaaS Security and Data Privacy
- 8. SaaS and Cloud Computing: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
- 9. The Future of SaaS Software as a Service
- 10. Conclusion
Understanding the SaaS Business Model

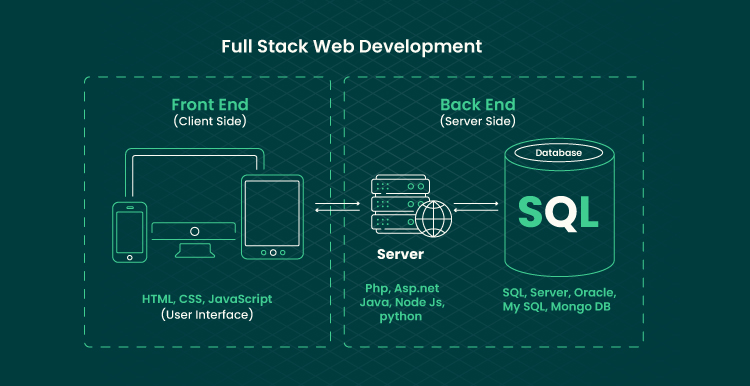
The SaaS software as a service model fundamentally transforms how businesses access and use software. Instead of the burdens associated with traditional software installations and maintenance, SaaS allows organizations to access applications via the internet on a subscription basis. This shift not only simplifies software management but also aligns with modern business needs for flexibility and collaboration.
Definition of SaaS and Core Components
SaaS stands for Software as a Service, a delivery model where software applications are hosted in the cloud and accessed through the internet. Key components of this model include:
- Subscription-Based Pricing: Users pay a recurring fee, which can be structured monthly, annually, or tiered based on usage.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Applications are hosted on cloud servers, enabling access from any internet-connected device.
- Automatic Updates: Providers manage software updates and maintenance, ensuring users always have the latest features.
Comparison with Traditional Software Licensing
When contrasting SaaS with traditional software licensing, several distinctions arise:
- Perpetual Licenses vs. Subscription: Traditional software often requires a one-time purchase, while SaaS is based on a subscription model, making it easier for businesses to manage budgets and predict expenses.
- Maintenance and Support: With traditional software, users bear the responsibility for updates and maintenance. In contrast, SaaS providers handle these tasks, freeing up internal IT resources.
The Role of Cloud Computing in SaaS Delivery
The advent of cloud computing has been pivotal in the growth of SaaS solutions. By leveraging cloud technology, SaaS applications offer enhanced scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, making them attractive to businesses of all sizes.
Key Characteristics and Benefits of SaaS
SaaS software as a service comes with numerous advantages that cater to modern business needs. Understanding these benefits is essential for business owners looking to optimize their operations.
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the primary benefits of SaaS is its cost efficiency. Businesses can avoid large upfront costs associated with traditional software purchases and instead opt for predictable monthly or annual expenses. For example, a mid-sized company may eliminate the need for on-premise server maintenance and licensing fees by adopting a SaaS solution like Microsoft 365. This transition could result in savings of thousands of dollars annually, as they no longer need to invest in physical hardware or worry about associated upkeep costs.
Scalability and Flexibility
SaaS solutions provide unparalleled scalability. Organizations can easily adjust their subscription levels based on current demands, making it ideal for growing businesses that experience fluctuating needs. For instance, a marketing agency may scale its CRM system during peak campaign seasons to accommodate increased user access and data processing requirements, only to scale back once the campaign concludes. This ability to dynamically adapt resources ensures that businesses can efficiently manage their operational costs without being locked into long-term commitments.
Accessibility
SaaS empowers employees to work seamlessly from anywhere—a coffee shop, a co-working space, or even a remote mountain cabin. This level of accessibility is vital in today’s increasingly mobile work environment, enabling teams to collaborate in real-time regardless of geographical barriers.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance
With SaaS, users benefit from automatic updates and maintenance managed by the provider. This means businesses can focus on their core operations without worrying about software management. For example, users of platforms like Salesforce or Google Workspace automatically receive new features and security patches without needing to take any action, ensuring that they always operate with the latest tools.
Improved Collaboration
SaaS applications often feature collaborative tools that enhance teamwork. Multiple users can access the same platform simultaneously, facilitating better communication and project management. Tools like Slack and Zoom exemplify this, providing integrated environments for messaging, video conferencing, and file sharing that keep teams connected and productive.
Counterargument to Cost-Effectiveness
Despite the apparent cost savings associated with SaaS, it’s essential to recognize potential hidden costs. For instance, businesses might incur integration fees when connecting SaaS applications with existing systems, data migration expenses when transferring information to the new platform, and potential vendor lock-in costs if they wish to switch providers later. These factors can diminish some of the initial cost advantages and require careful consideration during the decision-making process.
Counterargument to Scalability and Flexibility
While SaaS offers significant scalability benefits, very large enterprises with highly specialized needs may face limitations. For such organizations, on-premise solutions might provide greater control and customization capabilities, particularly when dealing with complex applications that require specific configurations. In these cases, the trade-off between flexibility and control must be evaluated thoroughly.
Popular SaaS Applications and Examples
SaaS applications span various industries, offering tailored solutions to meet diverse business needs. Below are some notable SaaS software as a service examples that highlight its versatility.
2. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-a-students-guide-to-securing-a-virtual-private-server-free
4. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-paas-in-cloud-computing-a-complete-guide-for-it-managers
5. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-your-ultimate-guide-to-virtual-private-server-windows-for-smbs
CRM Applications
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software is crucial for managing client interactions. Popular SaaS CRM applications include Salesforce , known for its robust analytics and AI capabilities, and HubSpot, which excels in inbound marketing and automation. Both platforms help businesses track customer data, manage leads, and automate marketing efforts efficiently.
Project Management Tools
For effective project management, applications like Asana and Trello provide user-friendly interfaces for tracking progress and enhancing team collaboration. Asana offers advanced project tracking features, while Trello’s visual boards simplify task management, allowing teams to streamline workflows and improve productivity.
Marketing Automation Platforms
SaaS applications such as Mailchimp and Marketo allow businesses to automate marketing campaigns, manage email lists, and analyze customer engagement. These tools are essential for modern marketing strategies, helping organizations reach their target audiences effectively.
Accounting and Finance Solutions
SaaS platforms like QuickBooks and Xero enable businesses to manage their finances more effectively. QuickBooks simplifies accounting processes with features like invoicing and expense tracking, while Xero provides real-time financial insights and robust reporting tools.
Human Resource Management Tools
Human Resource Management (HRM) applications like BambooHR and Gusto assist businesses in managing employee data, payroll, and recruitment processes, enhancing HR efficiency. BambooHR is particularly noted for its intuitive user interface and comprehensive reporting capabilities, while Gusto stands out for its payroll and benefits management features.
Industry-Specific SaaS Examples
SaaS applications also cater to specific industries. For instance, healthcare solutions like Epic and Cerner offer functionalities tailored to managing patient records, while educational institutions utilize platforms like Canvas and Blackboard for learning management. These industry-specific solutions demonstrate the versatility of SaaS in addressing unique business challenges.
Choosing and Implementing the Right SaaS Solution
Selecting the right SaaS platform for your business involves careful evaluation and consideration. Below are essential steps to guide business owners in this process.
Assessing Business Needs
Start by conducting a comprehensive assessment of your business operations. Identify areas where SaaS applications can provide the most significant benefit, considering team size, existing tools, and specific challenges. This understanding will help you determine which features are most important for your organization.
Evaluating SaaS Vendors
When evaluating potential SaaS vendors, consider the following criteria:
Features and Functionality
Ensure that the software aligns with your business needs and offers necessary features. For example, if your team requires strong reporting capabilities, confirm that the vendor provides customizable reporting tools.
Pricing Models
Analyze the pricing structure, including whether it is based on the number of users, storage, or features. Understanding the total cost of ownership will help you avoid unexpected expenses.
Customer Support
Assess the level of customer support offered by the vendor, including service level agreements (SLAs) and availability of assistance. A vendor that offers robust support can significantly ease the transition and ongoing use of their software.
Security Measures
Investigate the security protocols in place to protect your data. Look for certifications like ISO 27001 or compliance with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA to ensure your data is handled responsibly.
Integration Capabilities
Consider how well the SaaS solution integrates with your existing systems. A solution that seamlessly connects with your current tools will minimize disruption and improve efficiency.
Understanding SaaS Platform Options
Familiarize yourself with various SaaS platforms available in the market. This understanding will aid in making informed decisions that align with your business objectives and operational requirements.
Integration with Existing Systems
Ensure that the chosen SaaS solution can integrate seamlessly with your current systems. Data migration strategies should also be considered to ensure a smooth transition, including planning for any potential data loss or compatibility issues.
1. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-paas-in-cloud-computing-a-complete-guide-for-it-managers
2. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-a-students-guide-to-securing-a-virtual-private-server-free
5. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-your-ultimate-guide-to-virtual-private-server-windows-for-smbs
SaaS Security and Data Privacy
As businesses increasingly adopt SaaS solutions, security and data privacy are paramount. Understanding the shared responsibility model is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information.
The Shared Responsibility Model
In the shared responsibility model, SaaS providers are responsible for the security of the cloud infrastructure, while users are responsible for managing access to their data. This division highlights the importance of collaboration between both parties to ensure comprehensive data protection.
Security Measures Implemented by SaaS Providers
Reputable SaaS providers implement various security measures to protect user data, including:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implementing role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting frequent audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, which helps build trust with users.
Best Practices for Enhancing SaaS Security
To bolster the security of SaaS applications, businesses should adopt best practices, such as:
- Using Strong Passwords: Encourage employees to use complex passwords and change them regularly to reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication: Adding an extra layer of security to user accounts can significantly enhance protection against breaches.
- Conducting Regular Security Reviews: Periodically assessing security measures and protocols helps organizations stay ahead of potential threats.
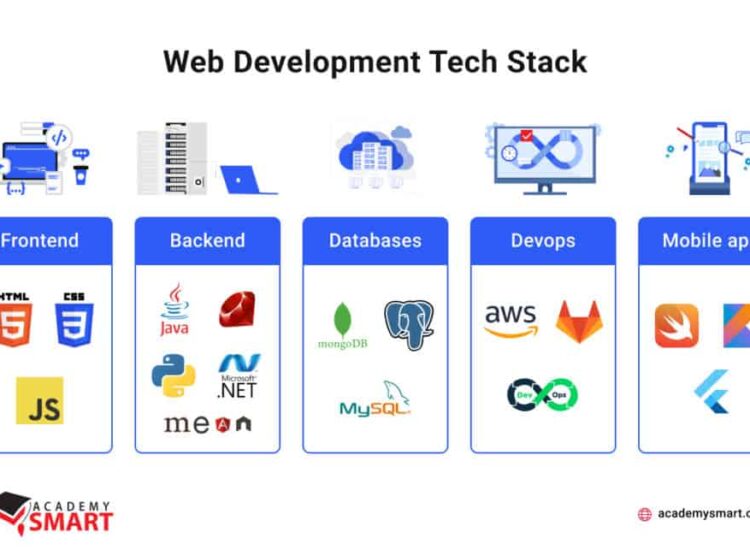
SaaS and Cloud Computing: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Understanding the relationship between SaaS and the broader cloud computing landscape is essential for business owners. SaaS is a significant subset of cloud computing, which encompasses various service models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS).
Defining IaaS and PaaS
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, enabling businesses to rent servers and storage. This model allows companies to manage their applications and data while the cloud provider handles the underlying infrastructure.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform for developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. This model supports rapid application development and facilitates testing and deployment.
Comparing and Contrasting IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
While IaaS provides the fundamental infrastructure needed to run applications, and PaaS offers a platform for development, SaaS delivers ready-to-use applications that require minimal IT management. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses choose the right cloud model based on their specific operational requirements.
Software as a Service in Cloud Computing
SaaS is integral to the cloud computing ecosystem, providing businesses with a flexible and cost-effective solution for accessing software applications. As organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, SaaS will play a crucial role in shaping their operational strategies.
The Future of SaaS Software as a Service
The SaaS market is continually evolving, with emerging trends that are shaping its future. As businesses seek innovative solutions, several key developments are expected to influence the landscape.
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The incorporation of artificial intelligence and machine learning into SaaS applications is enhancing automation and decision-making capabilities. For example, Salesforce Einstein leverages AI to provide predictive analytics and personalized customer interactions, streamlining sales processes and improving customer engagement. This trend is leading to more personalized user experiences and improved operational efficiency.
Growth of Vertical SaaS Solutions
Tailored solutions for specific industries are gaining popularity. Vertical SaaS applications address unique challenges faced by businesses in various sectors, providing specialized functionalities that enhance productivity. Examples include Veeva for life sciences and Procore for construction management, both of which offer industry-specific tools that meet distinct operational needs.
Increased Focus on Customer Success
Organizations are increasingly prioritizing customer outcomes, leading SaaS providers to invest in initiatives that enhance user satisfaction and retention. This focus on customer success is vital for building long-term relationships, with companies implementing feedback loops and user training programs to ensure their clients can maximize the value of the software.
Rise of Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
The growing popularity of low-code/no-code platforms enables citizen developers to build custom applications without extensive coding skills. Tools such as Zapier and Airtable allow users to automate workflows and manage data with minimal technical knowledge, democratizing software development and fostering innovation within organizations.
Market Growth Projections
The global SaaS market is anticipated to experience substantial growth in the coming years. According to industry forecasts, the market value is expected to exceed $700 billion by 2030, reflecting the ongoing shift towards cloud-based solutions.
Conclusion
In summary, SaaS software as a service offers significant advantages for businesses, including cost efficiency, flexibility, and ease of use. However, it’s crucial for organizations to navigate the complexities of software selection and implementation carefully. By assessing business needs, evaluating vendors, and prioritizing security, business owners can effectively leverage SaaS solutions to drive growth and enhance operational efficiency. As you consider your options, explore specific SaaS solutions relevant to your industry to unlock further potential. The “SaaS full form” is Software as a Service, a model that continues to revolutionize how businesses operate, paving the way for innovative and agile workflows.