Application development faces increasing complexity and cost pressures. IT managers often struggle to balance innovation with infrastructure management. PaaS in cloud computing offers a solution by abstracting infrastructure concerns, allowing developers to focus on application logic. However, challenges such as vendor lock-in and security responsibilities require careful consideration. This article examines PaaS, comparing it to IaaS and SaaS, and exploring its features, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
Toc
- 1. Understanding PaaS: A Comparison with IaaS and SaaS
- 2. Key Features and Benefits of PaaS in Cloud Computing
- 3. Related articles 01:
- 4. Cost Optimization and Efficiency with PaaS
- 5. Security and Compliance in PaaS Environments
- 6. Choosing the Right PaaS Provider and Managing Vendor Lock-in
- 7. Migration Strategies and Best Practices for PaaS Adoption
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. Related articles 02:
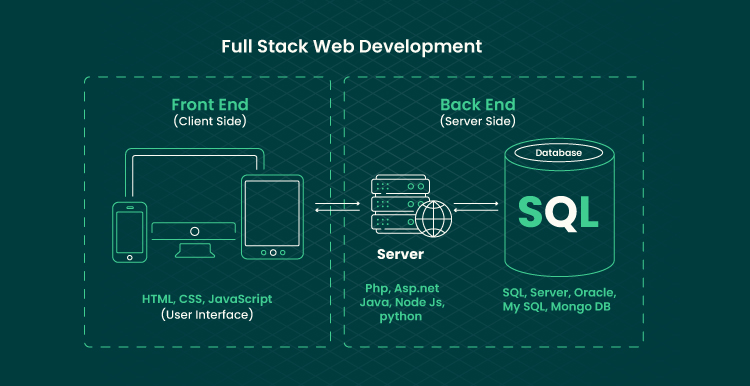
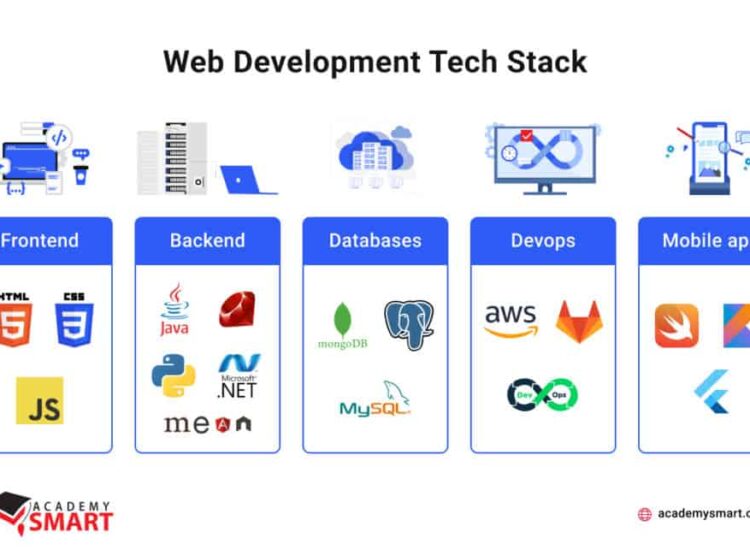
Understanding PaaS: A Comparison with IaaS and SaaS
To fully grasp the scope of PaaS in cloud computing, it’s essential to differentiate it from its counterparts: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each model caters to distinct organizational needs and plays a unique role in the cloud ecosystem.
Defining PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS
- PaaS: This model provides a platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. It includes tools for development, testing, and deployment, enabling faster and more efficient application development.
- IaaS: IaaS offers virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users manage everything from the operating system to applications, giving them greater control over their infrastructure but requiring more management effort.
- SaaS: SaaS delivers software applications over the internet, allowing users to access them without needing to install or maintain them on local devices. Users primarily manage data while the provider handles everything else.
Comparison Table
| Feature | PaaS in Cloud Computing | IaaS in Cloud Computing | SaaS in Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Platform for application development. | Virtualized computing resources. | Software applications delivered online. |
| User Control | Users manage applications and data. | Users manage OS, applications, and data. | Users only manage data. |
| Examples | Google App Engine, AWS Elastic Beanstalk. | AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure VMs. | Salesforce, Google Workspace. |
Use Cases for Each Model
Understanding when to use each model can significantly impact an organization’s success:
- When to Choose PaaS: Ideal for businesses focused on application development that need a platform to streamline their processes without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- When to Choose IaaS: Best for organizations that require extensive control over their infrastructure and are capable of managing operating systems and applications.
- When to Choose SaaS: Suitable for organizations looking for ready-to-use software solutions without the need for installation or maintenance. By understanding the distinctions between PaaS, IaaS, and SaaS, IT managers can make informed decisions about which service model best fits their organization’s needs.
Key Features and Benefits of PaaS in Cloud Computing
PaaS in cloud computing comes with a range of features that provide distinct advantages for IT managers and development teams. Here are some key features that make PaaS an attractive option:
Development Tools
PaaS platforms often include integrated development environments (IDEs), software development kits (SDKs), and application programming interfaces (APIs) that streamline the coding and debugging processes. These tools empower developers to work more efficiently and collaboratively.
Middleware and Integration Capabilities
PaaS solutions often incorporate middleware, which facilitates the integration of various applications and services. This capability simplifies data management and enhances overall application performance.
Database Management Services
Managed database services are a cornerstone of PaaS offerings. They enable developers to store, retrieve, and manage data effortlessly, reducing the complexity associated with database administration.
Security and Compliance Features
PaaS providers typically offer built-in security features such as data encryption, access control, and compliance with industry standards like HIPAA and GDPR. This allows organizations to focus on development while ensuring data protection.
Scalability and Elasticity
One of the most significant advantages of PaaS is its scalability. Organizations can dynamically allocate resources based on demand, ensuring optimal application performance even during peak usage periods.
Automation Capabilities
PaaS platforms often automate routine tasks such as deployment, scaling, and monitoring. This automation frees developers from mundane tasks, allowing them to concentrate on building innovative applications.
1. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-a-students-guide-to-securing-a-virtual-private-server-free
3. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-saas-software-as-a-service-a-comprehensive-guide-for-business-owners
5. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-your-ultimate-guide-to-virtual-private-server-windows-for-smbs
Cost-Effectiveness
With pay-as-you-go pricing models, PaaS can significantly reduce upfront hardware costs and ongoing operational expenses. Organizations can scale their resources according to their needs, leading to better cost management. Serverless Computing within PaaS An emerging trend within PaaS is serverless computing, which offers a cost-saving potential by charging only for actual compute time used. Unlike traditional virtual machines (VMs) that charge for allocated resources regardless of usage, serverless platforms like AWS Lambda allow organizations to pay only for what they consume, optimizing cost efficiency.
Faster Time to Market
By leveraging the features and tools offered by PaaS, organizations can accelerate their development cycles, enabling quicker deployment of applications and faster iterations based on user feedback.
Cost Optimization and Efficiency with PaaS
PaaS in cloud computing enhances development efficiency while providing substantial cost benefits for organizations. Here’s a closer look at how adopting PaaS can lead to financial optimization:
Detailed Cost Breakdown
- Reduced Hardware Investment: PaaS eliminates the need for organizations to invest heavily in physical servers and infrastructure, alleviating a significant financial burden.
- Lower Maintenance Expenses: Since PaaS providers manage the underlying infrastructure, organizations can minimize in-house IT maintenance costs.
- Flexible Pricing : The pay-as-you-go pricing model allows organizations to pay only for the resources they utilize, promoting cost efficiency. Current Trend: Growing Adoption of Serverless Computing The rise of serverless computing within PaaS is notable, as it supports a pay-per-use model and reduces operational overhead. This trend reflects a significant shift toward optimizing resource utilization and minimizing costs.
ROI Calculation Methodology
To determine the return on investment (ROI) from adopting PaaS, organizations should assess both initial and ongoing costs against the savings gained through increased efficiency and reduced operational expenses. A well-structured ROI analysis can provide valuable insights into the financial viability of transitioning to a PaaS model.
Case Studies Demonstrating Cost Savings
- E-commerce Transformation: An e-commerce platform that migrated to a PaaS solution reduced its application deployment time from weeks to hours, resulting in a 40% increase in user engagement due to enhanced performance.
- Healthcare Application Development: A healthcare provider utilized PaaS to develop a patient management system, benefiting from built-in compliance features and rapid iteration capabilities, which improved patient satisfaction.
Addressing Hidden Costs
While PaaS can lead to significant cost savings, organizations must be aware of potential hidden costs. Data transfer fees and egress charges can offset savings, and complex application migrations may incur unexpected expenses. Understanding these costs is crucial for effective budget management.
Strategies for Optimizing PaaS Costs
- Regular Usage Monitoring: Keep track of resource usage to identify underutilized services that can be scaled down.
- Optimizing Resource Allocation: Leverage automation tools to dynamically adjust resources based on real-time demand.
- Choosing the Right Pricing Model: Analyze pricing options to find the most cost-effective solution for your organization’s specific needs.
Security and Compliance in PaaS Environments

Security is a paramount concern for IT managers when considering PaaS solutions. Understanding the shared responsibility model and implementing best practices is essential for protecting sensitive data.
In a PaaS environment, security responsibilities are shared between the provider and the client. While the provider secures the underlying infrastructure, clients must ensure their applications and data are adequately protected.
Security Features Offered by PaaS Providers
PaaS providers typically offer robust security features, including:
- Access Control: Role-based access control systems ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
- Data Encryption: Encryption protocols protect data both at rest and in transit, safeguarding against unauthorized access.
- Intrusion Detection Systems: These tools monitor for suspicious activity, providing alerts for potential security breaches.
Compliance with Industry Standards
PaaS can help organizations meet various compliance standards, such as HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS. However, organizations must ensure that their applications comply with relevant regulations, often requiring additional measures to manage data privacy effectively.
Best Practices for Securing PaaS Environments
To enhance security within PaaS environments, organizations should consider implementing the following best practices:
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct routine audits and vulnerability assessments to identify potential security risks.
- Application Updates: Ensure all applications are regularly updated and patched to address vulnerabilities.
- Employee Security Training : Provide training to employees to raise awareness about potential threats and best practices for data protection. Counterpoint on Security Responsibilities While PaaS providers offer security features, the ultimate responsibility for data security and compliance still rests with the client. Organizations must invest in ongoing efforts and resources to ensure adequate protection of their data and applications.
Addressing Data Sovereignty and Residency Concerns
Organizations must also consider data sovereignty and residency issues, ensuring that data storage and processing comply with local regulations.
Choosing the Right PaaS Provider and Managing Vendor Lock-in
Selecting the right PaaS provider is crucial for maximizing the benefits of cloud computing while minimizing risks associated with vendor lock-in.
Key Selection Criteria
When evaluating PaaS providers, IT managers should consider several key factors:
- Features and Functionality: Ensure the provider offers the necessary tools and services to meet specific development needs.
- Cost Structure: Analyze pricing models to find a solution that aligns with budgetary constraints.
- Security and Compliance: Evaluate the provider’s security measures and compliance capabilities.
- Support Services: Look for providers that offer robust support services to assist with any potential issues.
Notable PaaS Providers
Several leading PaaS providers are making significant impacts in the cloud computing landscape:
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk: A flexible solution for deploying and managing applications.
- Google App Engine: A scalable platform that allows developers to build and host applications in Google’s cloud.
- Microsoft Azure: Offers a comprehensive suite of services for application development and deployment.
- Heroku: A platform that enables developers to build, run, and operate applications entirely in the cloud.
- OpenShift: An enterprise-level PaaS solution that provides a robust environment for developing and deploying applications.
Strategies for Mitigating Vendor Lock-in
Vendor lock-in can pose challenges for organizations that adopt PaaS solutions. To mitigate this risk, consider the following strategies:
- Using Open Standards: Opt for platforms that adhere to open standards to facilitate easier migration.
- Developing Portable Applications: Focus on building applications that can transition seamlessly between different PaaS providers.
- Implementing a Multi-Cloud Strategy : Consider using multiple cloud providers to distribute workloads and avoid dependency on a single vendor. For instance, organizations can leverage AWS for certain services while using Azure for others, enhancing flexibility and reducing reliance on one provider. Current Trend: Kubernetes and Containerization The prevalence of Kubernetes as a container orchestration platform within many PaaS offerings is notable. Kubernetes improves portability and scalability, enabling organizations to deploy applications across multiple environments seamlessly.
Discussion of Contract Terms and SLAs
Before committing to a PaaS provider, organizations should carefully review contract terms and service level agreements (SLAs) to understand the provider’s obligations regarding uptime, support, and data security. Counterpoint on Migration Challenges While evaluating PaaS providers, organizations should be aware of the difficulties in migrating away from a chosen provider due to potential data migration complexities and application refactoring needs. This challenge highlights the importance of choosing the right provider from the outset.
Migration Strategies and Best Practices for PaaS Adoption
Migrating to a PaaS environment requires careful planning and execution. Here are some strategies and best practices to ensure a smooth transition:
Different Migration Strategies
- Lift-and-Shift Migration: This approach involves moving existing applications to the cloud with minimal changes, making it a quick and straightforward option.
- Refactoring: Modify applications to take full advantage of PaaS capabilities, optimizing performance and functionality.
- Rebuilding: Develop new applications from scratch specifically for the PaaS environment, allowing for maximum efficiency and scalability.
Planning and Execution Phases
Successful PaaS migration involves thorough planning and execution. Organizations should outline their migration objectives, identify key stakeholders, and develop a detailed timeline for the transition.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
- Conduct Thorough Testing: Before fully migrating, conduct testing to ensure applications function correctly in the new environment.
- Training and Support: Provide training for development teams to familiarize them with the new platform and tools.
- Phased Migration: Consider a phased approach to migration, allowing for adjustments based on feedback and performance metrics.
Addressing Potential Challenges
During migration, organizations may encounter challenges such as data transfer issues or application compatibility. Being proactive in addressing these challenges can help minimize disruptions.
Importance of Thorough Testing and Validation
Testing and validation are crucial for ensuring that applications operate as intended in the PaaS environment. Organizations should establish clear testing protocols to identify and resolve issues before full deployment.
Conclusion
PaaS in cloud computing presents a powerful solution for IT managers seeking to enhance their application development processes. By understanding the key features, advantages, and challenges of PaaS, organizations can make informed decisions that lead to improved efficiency, cost savings, and scalability. As cloud computing continues to evolve, embracing PaaS can position businesses for success in an increasingly competitive landscape. Evaluating current IT infrastructures and considering PaaS adoption can provide organizations with the tools needed to meet their unique needs. By leveraging PaaS, IT managers can navigate the complexities of modern application development while focusing on driving innovation and growth within their organizations. The integration of serverless computing, AI/ML capabilities, and Kubernetes further underscores the relevance of PaaS in today’s technology landscape, making it a critical component for businesses aiming to thrive in the digital age.
2. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-your-ultimate-guide-to-virtual-private-server-windows-for-smbs
3. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-saas-software-as-a-service-a-comprehensive-guide-for-business-owners
5. https://tech.banktop.vn/mmoga-a-students-guide-to-securing-a-virtual-private-server-free